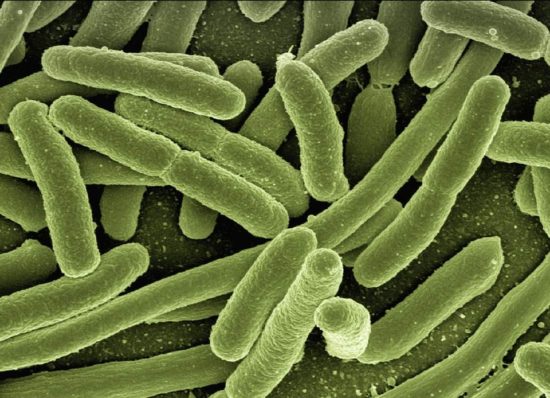
Two codependent routes lead to high-level MRSA
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) exhibits resistance to β-lactam antibiotics due to the acquisition of penicillin-binding protein 2a (PBP2a). In antibiotic-administered conditions, MRSA adopts an alternative cell division mode and alters the peptidoglycan architecture at the division septum. This resensitizing agent interferes with these mechanisms, offering new interventions.
AMR NEWS
Your Biweekly Source for Global AMR Insights!
Stay informed with the essential newsletter that brings together all the latest One Health news on antimicrobial resistance. Delivered straight to your inbox every two weeks, AMR NEWS provides a curated selection of international insights, key publications, and the latest updates in the fight against AMR.
Don’t miss out on staying ahead in the global AMR movement—subscribe now!